Discover how your gut microbiota influences digestion and emotional wellbeing. Learn how nutrition and lifestyle choices can nurture your gut health and balance your mind.
Introduction
Your gut is home to trillions of microorganisms that silently influence your overall health, collectively weighing over a kilogram. This intricate ecosystem, the gut microbiota, is as unique as your fingerprint or DNA. From influencing digestion and immunity to impacting mood and brain function, your gut bacteria play a significant role in your well-being. This article will explore the development of your microbiota, the factors that affect it, and the importance of nurturing it for a healthier body and mind.
What Determines Your Gut Microbiota?
Your microbiota’s journey begins at birth, and the method of your birth significantly influences your initial set of gut microbes.
Vaginal Birth: Babies born vaginally acquire bacteria from their mother’s vaginal microbiota, particularly lactobacilli, which promote gut balance.
Caesarean Birth: Babies delivered via C-section acquire bacteria from their surroundings—the doctor’s skin, hospital surfaces, and the mother’s skin—resulting in a more diverse but sometimes less stable microbiome.
Over time, your diet, environment, and lifestyle shape this microbiota into a unique ecosystem that evolves throughout your life.
How the Microbiota Changes with Age
As we age, our gut microbiota naturally changes. A reduction in microbial diversity has been linked to ageing, inflammation, and frailty. Maintaining a wide variety of beneficial bacteria is crucial for vitality and resilience. Key factors that affect the microbiota include:
- Stress: Chronic stress disrupts gut balance, leading to digestive and emotional disturbances.
- Medications: Antibiotics and other common drugs can dramatically alter gut bacterial populations.
- Diet & Exercise: Fibre-rich foods and regular movement support microbial diversity and metabolic health.
Your daily lifestyle choices truly define how your microbiome ages with you.
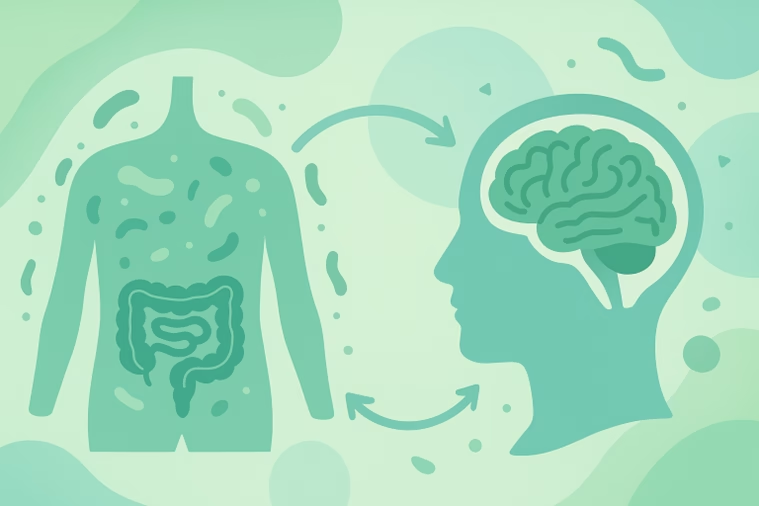
The Gut-Brain Connection: When Your Second Brain Talks Back
The communication pathway between your gut and your brain—known as the gut-brain axis—demonstrates the interconnectedness of your digestion and emotions.
- The Vagus Nerve: The Mind-Body Messenger
The vagus nerve carries constant messages between your brain and gut. Beneficial bacteria like lactobacilli use this nerve to send signals that can calm the mind and regulate mood.
- Serotonin & Tryptophan: The Mood Regulators
Gut microbes help produce tryptophan, an amino acid needed to make serotonin—the “happy hormone” that regulates mood, sleep, and appetite. Species like bifidobacteria boost tryptophan levels, helping maintain emotional stability.
- Short-Chain Fatty Acids: Small but Mighty Molecules
When you eat fibre, your gut microbes ferment it to form short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) like butyrate, acetate, and propionate. These molecules fuel your intestinal cells and even affect brain gene expression—improving focus, reducing inflammation, and supporting emotional balance.
Your microbiota and brain exist in symbiosis: you feed your microbes, and they, in turn, nourish your mind.
Ways to Improve and Modify Gut Microbiota
While we cannot change our human DNA, we can absolutely influence the genes of our gut microbes. Here’s how:
- Eat for Your Microbes
A diet high in fibre, fruits, vegetables, and whole grains feeds the good bacteria in your gut. These foods act as prebiotics, fuelling microbial diversity and health.
- Add Probiotics and Live Biotherapeutics
Probiotics—live beneficial bacteria—can restore gut balance and support mood. From yoghurt and kefir to kombucha and fermented veggies, probiotic-rich foods are nature’s gut therapy. Clinically, probiotics are now referred to as live biotherapeutics due to their therapeutic potential in improving gut and brain function.
- Feacal Microbiota Transplantation (FMT)
In severe medical cases, such as chronic C. difficile infections, doctors use FMT—transferring gut bacteria from healthy donors to patients to restore microbial health.
- Be Mindful with Medications
Over 75% of prescription drugs impact the gut microbiota. Discussing medication choices and gut-protective measures with your doctor can help you maintain microbial balance.
Gut Health Meets Mental Health: The Psychobiotic Revolution
Emerging research reveals that gut microbes may influence conditions like anxiety, depression, autism, and even Parkinson’s disease. This has given rise to the exciting field of psychobiotics—probiotics that support mental health.
The Science Behind Psychobiotics
Bifidobacterium longum (B. longum): Animal studies showed that mice taking this strain were less anxious and had better cognition. In human trials, participants reported reduced stress and improved sleep quality.
Probiotics in Pregnancy: Expectant mothers who took probiotics for six months reported fewer symptoms of postpartum depression than those who didn’t.
While not all probiotics work the same way in every individual, these findings highlight the gut microbiota as a promising target for mental wellness interventions.
The Role of Stress and the Gut
Chronic stress not only disrupts emotional balance but also disturbs gut bacteria. In turn, an imbalanced microbiota can heighten anxiety, creating a vicious gut-stress loop. Fortunately, research shows that restoring gut balance through probiotics, nutrient-dense foods, and mindfulness practices can improve stress resilience and emotional health.
The Future of Gut-Based Wellness
The relationship between the gut and brain is one of the most groundbreaking discoveries in modern health science. Clinical research, such as that conducted by Atlantia Clinical Trials, continues to explore how nutrition, microbiota modulation, and probiotics influence both mental and physical health outcomes. At Nutrify Your Gut, we aim to translate this science into everyday nutrition—empowering you to take control of your health through a balanced gut ecosystem.
In Summary
- Your gut microbiota is more than just bacteria—it’s a living organ that influences digestion, immunity, and even emotions.
- It starts shaping at birth and evolves with lifestyle.
- It communicates with your brain via nerves, neurotransmitters, and metabolites.
- It can be strengthened through diet, probiotics, and mindful living.
- By caring for your gut, you nurture not just your body—but also your mind, mood, and longevity.
✨ At Nutrify Your Gut, we believe a healthy gut is the foundation of holistic wellness. Feed your microbes—and they’ll take care of you. ✨
Reference : Atlantia Clinical Trials (2025, March 05). The role of gut bacteria on mental health.
Suggested Tags: Gut Health, Microbiome, Probiotics, Gut-Brain Axis, Mental Health, Psychobiotics, Holistic Wellness
Slug/URL suggestion: /blog/how-gut-microbiota-shapes-health-and-mind


